
While tennis elbow will not show up in X-rays, they can be used to detect other conditions, such as bone fractures, joint misalignment, or one or more types of arthritis.
While tennis elbow usually does not require diagnostic imaging, additional scan tests may be ordered to rule out other possible causes of the patient's symptoms. 5 The doctor may also ask patients to hold their affected arm out straight and then press their hand and fingers back to see if this causes pain, 3 and may also test the elbow and arm's range of motion to rule out joint damage or nerve entrapments.
#How to read mri images of elbow skin#
The patient's skin may be inspected for signs of rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis, and blood may be taken to check for signs of these or other autoimmune disorders. The doctor may test nerve reflexes with a hammer, and will also inspect bone and joint alignment. Generally, lateral epicondylitis is suspected when the doctor pushes on the lateral epicondyle (or bump on the outside of your elbow) and your pain is reproduced. During the physical exam, the doctor will visually inspect and touch the patient's elbow and arm-and possibly other joints in the body, depending on what diagnosis he or she suspects.
Similarly, for parts of the body that have many similar features repeated multiple times, a difference in one of the features can be a sign that something is amiss.
#How to read mri images of elbow Patch#
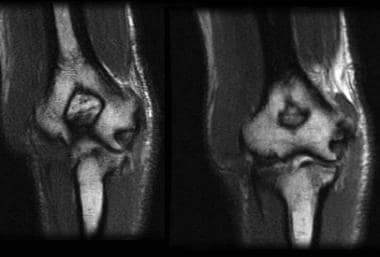
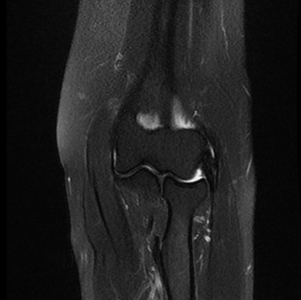
If, in your MRI, you notice a patch of lightness or darkness on one side of your body that does not match what's on the other side, this can be cause for concern. By and large, the body is very symmetrical. Here, you're basically viewing thin slices of your body from the top down - as if you've been cut into many thin horizontal slices from your head to your toes like a salami. Cross-sectional: Often the hardest for non-doctors to interpret.You're looking at your features vertically from the front - as if you were standing facing the camera. Coronal: These images are basically a "head on" view of your body.The image is as if you've been sliced in half vertically, from your head to your pelvis. Sagittal MRIs are basically side or profile views of your body. Sagittal: Often the easiest for non-doctors to interpret.The three main ways MRIs are displayed are: X Research source

Knowing how MRIs are shot can help you make sense of your images. However, in many cases, the image you see may be a completely unintelligible mix of black, white, and grey. When your MRI first loads up, if you're lucky, it will be immediately obvious what you're looking at. Familiarize yourself with the different MRI viewing schemes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
